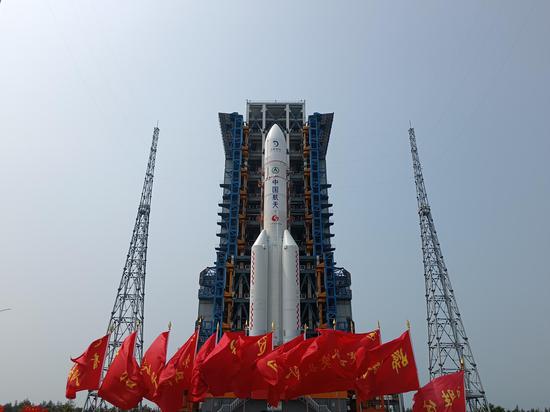
The Chang'e 6 robotic probe, tasked with the world's first attempt to retrieve samples from the moon's far side, embarked on its historic journey on Friday from China's southernmost province of Hainan.
A Long March 5 heavy-lift carrier rocket — the biggest and mightiest space vehicle in China, standing at 20 stories and weighing 870 metric tons — blasted off from its launch pad at 5:27 pm with the 8.35-ton Chang'e 6 spacecraft aboard and soared skyward, leaving hundreds of thousands of spectators awestruck at and around the coastal Wenchang Space Launch Center.
The liftoff marked the beginning of the country's second lunar sample-return expedition after the successful Chang'e 5 mission in the winter of 2020.
Yet the unfolding mission will be much more difficult, challenging and riveting than the Chang'e 5, which landed on the moon's near side, and will definitely be recorded — regardless of whether it is a huge success or an unfortunate failure — as a symbol of audacious and pioneering work in the history of humankind's lunar exploration.
Previously, 10 lunar sample-return missions were undertaken by the United States, the former Soviet Union and China, but all these samples were collected from the moon's near side.
As one of China's, and also the world's, most significant space journeys this year, major steps in the Chang'e 6 mission have made headlines around the globe and have garnered a lot of attention from the Chinese people.
The local tourism authority in Wenchang estimated at least 200,000 travelers arriving in Longlou, a township that is home to the launch complex, on Friday to witness the liftoff.
According to the China National Space Administration, after flying for about 37 minutes, the Long March 5 rocket successfully placed the robotic lunar probe into an Earth-moon transfer trajectory, the gateway to our celestial neighbor.
Complex operation
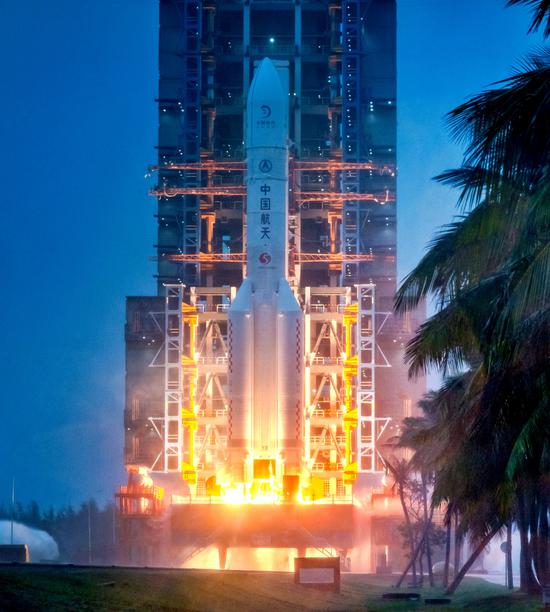

Within the next several days, the Chang'e 6 probe is programmed to fly along its moonward trajectory and make some correction operations before conducting a key braking maneuver to avoid accidentally flying past the moon. Thereafter, the spacecraft will be captured by the moon's gravity and move into a lunar orbit.
Like its predecessor, the Chang'e 6 spacecraft is designed and built by the Beijing-based China Academy of Space Technology, a subsidiary of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp, and also consists of four components — an orbiter, a lander, an ascender and a reentry capsule.
Its operational process will basically mimic that of the Chang'e 5 spacecraft. After the probe reaches lunar orbit, its components will separate into two parts, with the orbiter and reentry capsule remaining in orbit, while the lander and ascender start approaching the lunar surface.
When everything is ready, the lander-ascender combination will make a soft landing in the South Pole-Aitken Basin — a gigantic crater on the lunar far side and also the largest, oldest and deepest basin recognized on the moon. It will then start using a drill and a mechanical arm to gather surface and underground samples.
If everything proceeds smoothly, up to 2 kilograms of stones and soil will be collected and packed in a vacuum-sealed metal container inside the ascender.
After the collection operation is completed, the engines of the ascender will elevate it to lunar orbit for docking with the reentry capsule. The vacuum-sealed container carrying the samples will be transferred to the module before the ascender undocks.
The combination of orbiter and reentry capsule will then depart the lunar orbit and return to the Earth's orbit, where the pair will break up and the reentry capsule will conduct a host of complicated maneuvers to return to the Siziwang Banner Landing Site in the Inner Mongolia autonomous region.
The main difference between the Chang'e 5 and Chang'e 6 probes lies in their landing destination on the moon and corresponding technical issues, the most crucial of which is the communication difficulties between the lunar far side and Earth.
In order to establish a data link for the Chang'e 6 probe, China deployed a new relay satellite in the lunar orbit in March.
Wang Qiong, a deputy chief designer of the Chang'e 6 mission, said there will be a host of challenges and uncertainties during the 53-day expedition, adding that Chinese scientists and engineers have made efforts to work out the best available solutions.
"During the Chang'e 5 mission, the probe worked on the near side, so we could monitor its work processes and send control signals to it anytime. But in the case of Chang'e 6, we will have to depend solely on the Queqiao 2 relay satellite to transmit data and signals. The satellite has a limited coverage over the landing site, which will consequently restrict our communication with the Chang'e 6 probe," he said.
Wang said that engineers have applied some new advanced technologies in the mission, such as a rapid sampling system and a smart data-analysis mechanism, to ensure that the sample-collection tasks are effectively and efficiently completed on the lunar surface within shorter operating time.
In the case of a communications blackout, the Chang'e 6 probe is capable of conducting some key maneuvers in accordance with preset programs, he added.















































 京公网安备 11010202009201号
京公网安备 11010202009201号