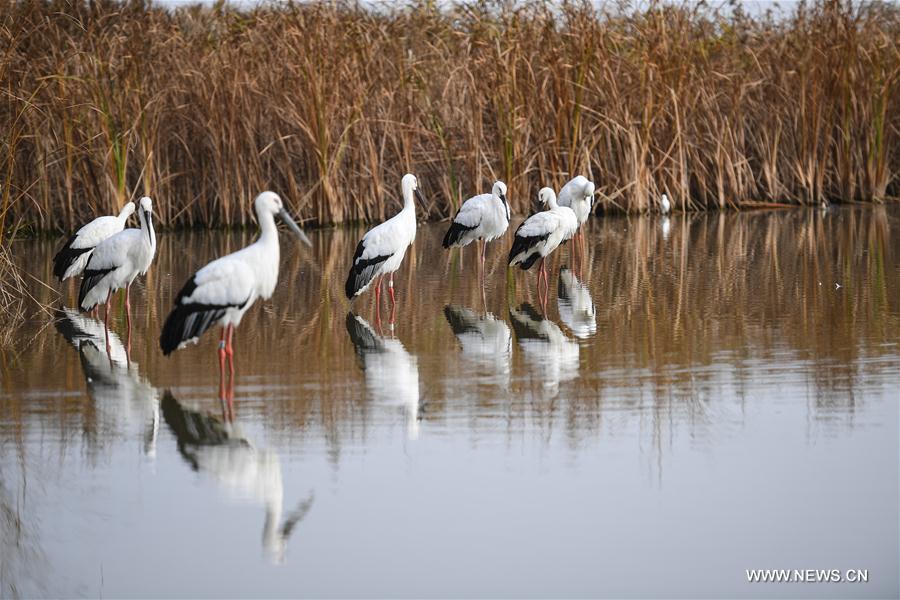
Wild birds are seen at the Yancheng Wetland and Rare Birds National Nature Reserve in east China's Jiangsu Province, Nov. 15, 2017. China's Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf (Phase I) were inscribed on the World Heritage List as a natural site on Friday at the ongoing 43rd session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee in Azerbaijan's capital of Baku. Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf of China are located in the Yellow Sea ecoregion, containing the world's largest continuous mudflat seashore. It is the central node of the East Asian-Australasian Flyway (EAAF), which is the most threatened migratory flyway worldwide and boasts the largest number of endangered and critically endangered species. The area has a high biodiversity, with about 280 species of fishes and more than 500 species of invertebrates, providing a variety of food resources for millions of migratory birds. (Xinhua/Ji Chunpeng)
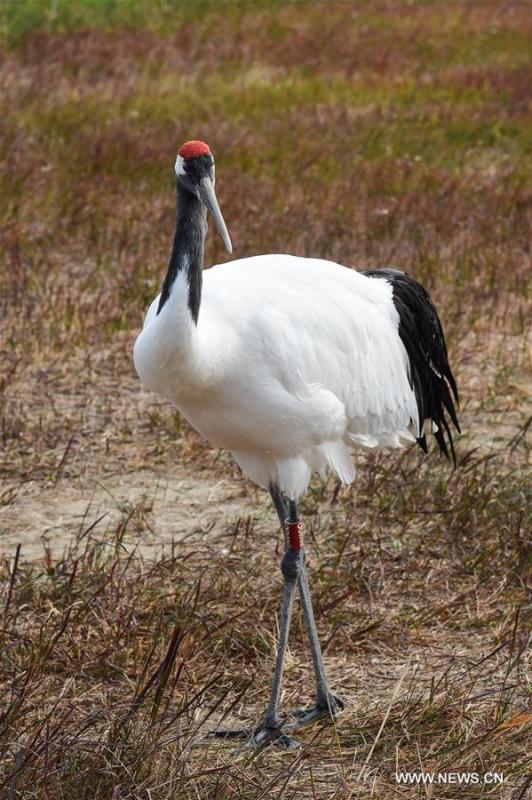

A red-crowned crane is seen at the Yancheng Wetland and Rare Birds National Nature Reserve in east China's Jiangsu Province, Nov. 15, 2017. China's Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf (Phase I) were inscribed on the World Heritage List as a natural site on Friday at the ongoing 43rd session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee in Azerbaijan's capital of Baku. Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf of China are located in the Yellow Sea ecoregion, containing the world's largest continuous mudflat seashore. It is the central node of the East Asian-Australasian Flyway (EAAF), which is the most threatened migratory flyway worldwide and boasts the largest number of endangered and critically endangered species. The area has a high biodiversity, with about 280 species of fishes and more than 500 species of invertebrates, providing a variety of food resources for millions of migratory birds. (Xinhua/Li Bo)
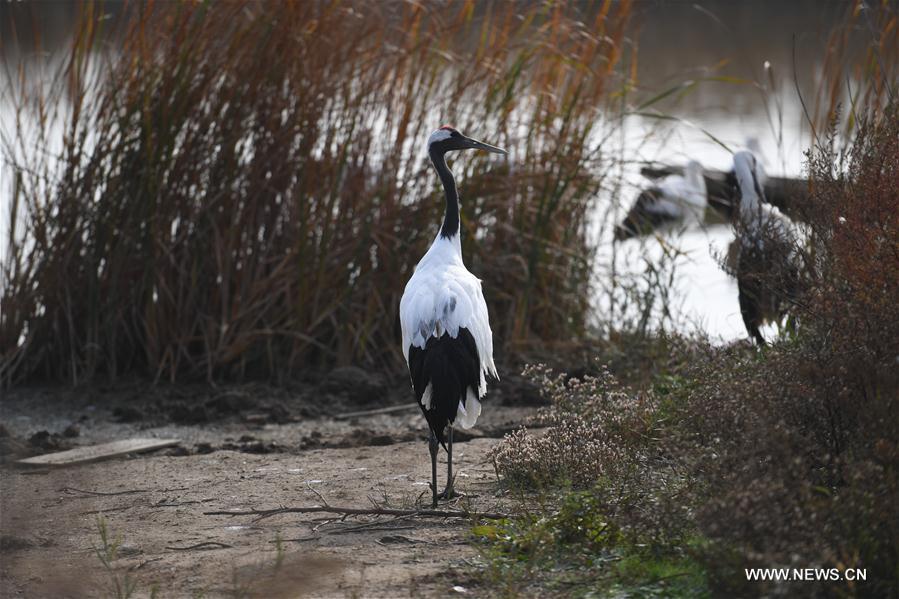

Red-crowned cranes are seen at the Yancheng Wetland and Rare Birds National Nature Reserve in east China's Jiangsu Province, Nov. 15, 2017. China's Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf (Phase I) were inscribed on the World Heritage List as a natural site on Friday at the ongoing 43rd session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee in Azerbaijan's capital of Baku. Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf of China are located in the Yellow Sea ecoregion, containing the world's largest continuous mudflat seashore. It is the central node of the East Asian-Australasian Flyway (EAAF), which is the most threatened migratory flyway worldwide and boasts the largest number of endangered and critically endangered species. The area has a high biodiversity, with about 280 species of fishes and more than 500 species of invertebrates, providing a variety of food resources for millions of migratory birds. (Xinhua/Ji Chunpeng)
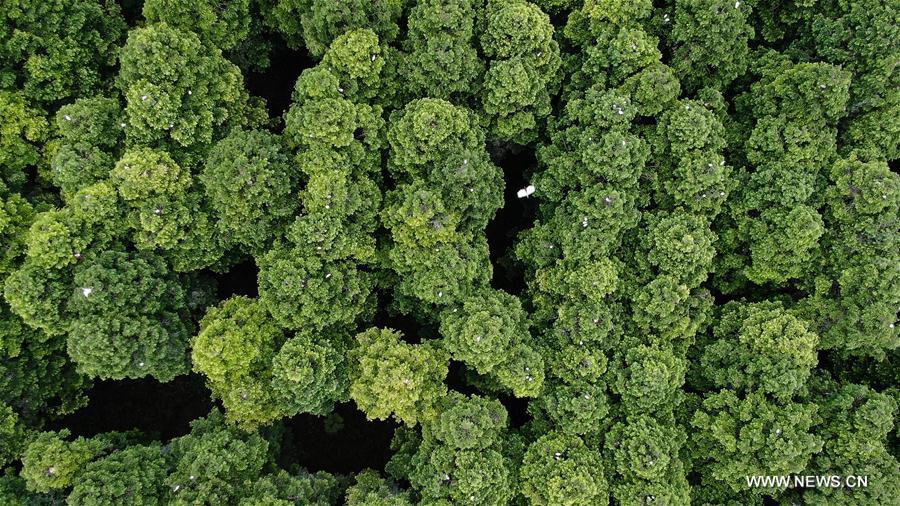

Aerial photo shows egrets resting on top of trees at the Dafeng Milu National Nature Reserve in the city of Yancheng, east China's Jiangsu Province, June 26, 2019. China's Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf (Phase I) were inscribed on the World Heritage List as a natural site on Friday at the ongoing 43rd session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee in Azerbaijan's capital of Baku. Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf of China are located in the Yellow Sea ecoregion, containing the world's largest continuous mudflat seashore. It is the central node of the East Asian-Australasian Flyway (EAAF), which is the most threatened migratory flyway worldwide and boasts the largest number of endangered and critically endangered species. The area has a high biodiversity, with about 280 species of fishes and more than 500 species of invertebrates, providing a variety of food resources for millions of migratory birds. (Xinhua/Li Xiang)
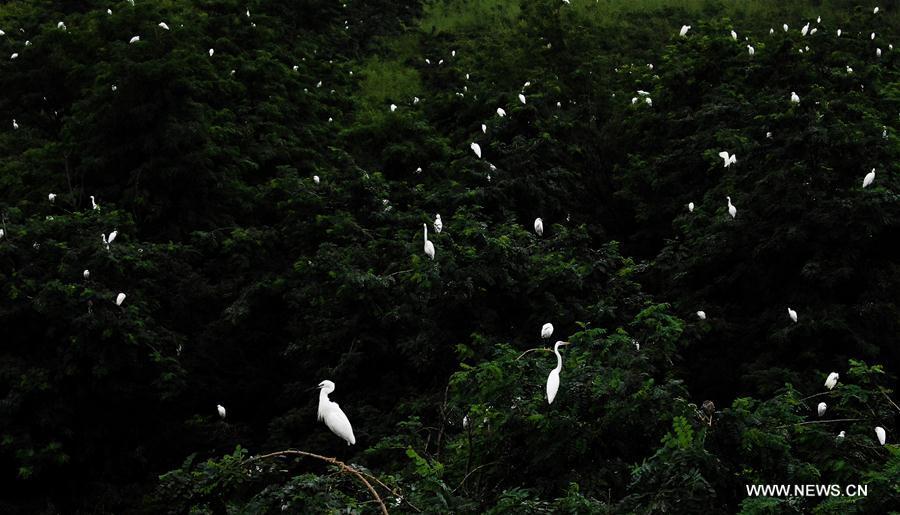

Aerial photo shows egrets resting on top of trees at the Dafeng Milu National Nature Reserve in the city of Yancheng, east China's Jiangsu Province, June 26, 2019. China's Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf (Phase I) were inscribed on the World Heritage List as a natural site on Friday at the ongoing 43rd session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee in Azerbaijan's capital of Baku. Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf of China are located in the Yellow Sea ecoregion, containing the world's largest continuous mudflat seashore. It is the central node of the East Asian-Australasian Flyway (EAAF), which is the most threatened migratory flyway worldwide and boasts the largest number of endangered and critically endangered species. The area has a high biodiversity, with about 280 species of fishes and more than 500 species of invertebrates, providing a variety of food resources for millions of migratory birds. (Xinhua/Li Xiang)
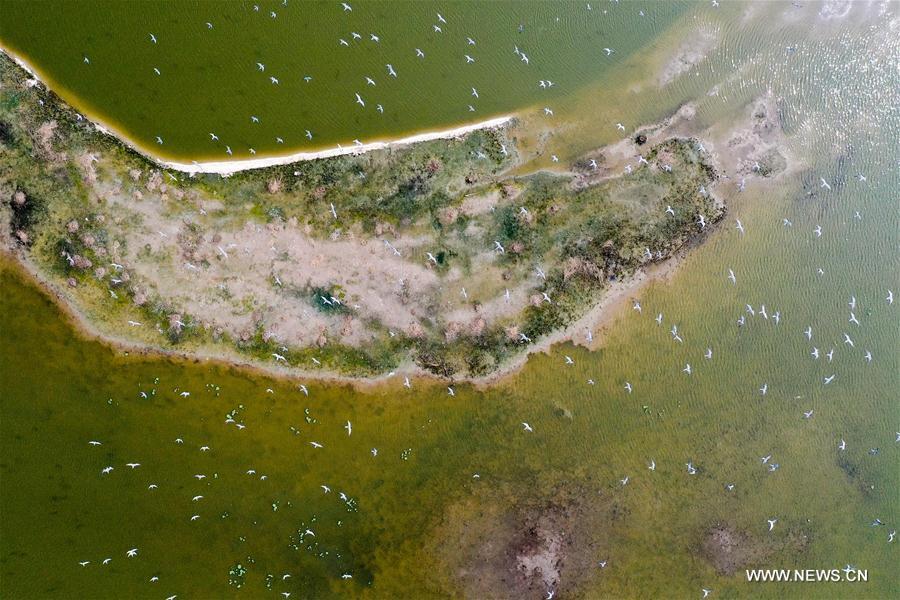

Aerial photo shows terns flying over the Dafeng Milu National Nature Reserve in the city of Yancheng, east China's Jiangsu Province, June 28, 2019. China's Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf (Phase I) were inscribed on the World Heritage List as a natural site on Friday at the ongoing 43rd session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee in Azerbaijan's capital of Baku. Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf of China are located in the Yellow Sea ecoregion, containing the world's largest continuous mudflat seashore. It is the central node of the East Asian-Australasian Flyway (EAAF), which is the most threatened migratory flyway worldwide and boasts the largest number of endangered and critically endangered species. The area has a high biodiversity, with about 280 species of fishes and more than 500 species of invertebrates, providing a variety of food resources for millions of migratory birds. (Xinhua/Li Bo)
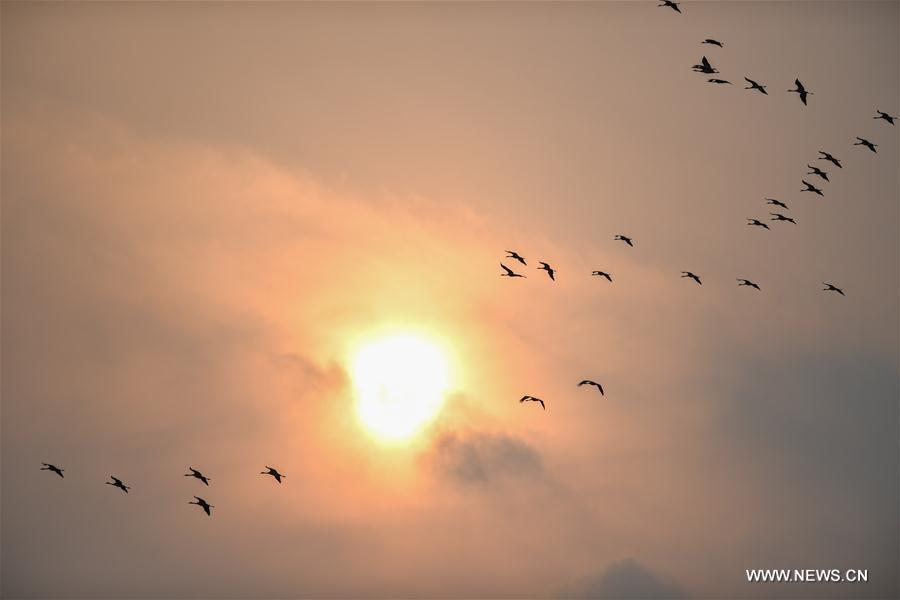

Wild birds fly over the Yancheng Wetland and Rare Birds National Nature Reserve in east China's Jiangsu Province, Nov. 15, 2017. China's Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf (Phase I) were inscribed on the World Heritage List as a natural site on Friday at the ongoing 43rd session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee in Azerbaijan's capital of Baku. Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the coast of the Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf of China are located in the Yellow Sea ecoregion, containing the world's largest continuous mudflat seashore. It is the central node of the East Asian-Australasian Flyway (EAAF), which is the most threatened migratory flyway worldwide and boasts the largest number of endangered and critically endangered species. The area has a high biodiversity, with about 280 species of fishes and more than 500 species of invertebrates, providing a variety of food resources for millions of migratory birds. (Xinhua/Ji Chunpeng)